1. Defrag using Defraggler
2. Malware checkup
3. Driver Checks
4. Remove AutoRun stuff + AutoRun & Revo Uninstaller free
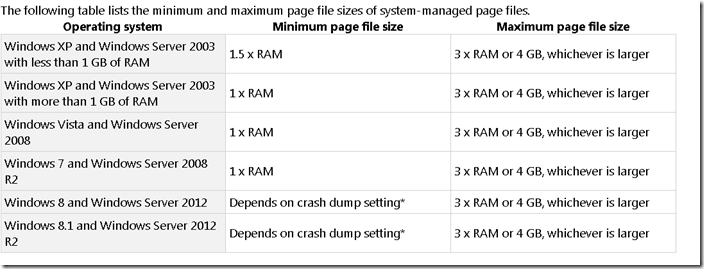
5. Tune Paging File : General Rules Max/Min=(RAM * 1.5) per This Windows SuperIUser post with MS Reference
and MS Best Practices for paging files accross Windows versions
more detailed Technical Insight from SysInternals Author!
Diagnostics:
a. Deterrmine Cause of performance issues during load using tools:
The size of your Paging File depends on the workload you are running.
The best advice can be found in this article:
http://blogs.technet.com/b/markrussinovich/archive/2008/11/17/3155406.aspx
It was written for Vista but is still true.
Run Process Explorer http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/bb896653 while running your maximum workload and monitor the peak commit charge on the memory tab of the System Information feature (ctrl+i).
b. Use Perfmon/Resource Monitor: check:
Commit Limit
Crash dump size
Perfmon: Add the following counters:
- Memory\Committed Bytes - Committed Bytes is the amount of committed virtual memory, in bytes.
- Memory\Committed Limit - Amount of virtual memory that can be committed without having to extend the paging file
- Memory\% Committed Bytes In Use - Ratio of Memory\Committed Bytes to the Memory\Commit Limit
The page file size formula should be:
(Max value of Committed Bytes + additional 20% buffer to accommodate any workload bursts)-RAM size
For example: If the server has 24 GB RAM and the maximum of Committed Bytes is 26 GB, then the recommended page file will be: (26*1.2)-24) = 7.2 GB
to bo continued…

No comments:
Post a Comment