Edge and Chrome browser Developer Utilities That I Need to Know
Every fashionable internet browser normally gives features for devs to debug internet apps. We use the chrome console to execute short code snippets for debugging and experimental purposes. For supporting to write down code snippets at the console productively, Chrome gives numerous productiveness-centered shortcuts just like the Bash interpreter, which reinforces developer productiveness on GNU/Linux terminals. We can use those Chrome console software shortcuts to hurry up internet utility debugging-associated tasks (i.e., Getting the chosen DOM detail withinside the inspector).
Speed up Selections with JQuery Selectors
Chrome lets you use $ syntax on the console even if you don’t use the JQuery library. On the Chrome console, $ works as a shortcut for the document.querySelector method by letting you instantly query for one element:
$('.item-01')The above code snippet prints the first DOM node that has the item-01 class name. Similarly, the $$ shortcut triggers the document.querySelectorAll method and returns more than one element. For example, the following code snippet prints all <h1> elements:
$$('h1')You can also select DOM elements based on XPath expressions as follows:
$x('/html/body/div')Console API Shortcuts
Every browser and JavaScript runtimes like Node.js offer a fully-featured console API for developers to use in web app codebases for debugging purposes. You can log some messages on the browser console when unexpected issues occur. Then, you can analyze them to diagnose critical issues during developer or user testing. console.log, console.error, and console.warn. are commonly used console logging methods.
Chrome offers console-only, shorthand function names for several console APIs to boost debugging productivity. The dir function triggers the console.dir API method, so you can use it to print key-value data in objects. This is a good mechanism to print DOM element properties when the console prints an element with its HTML code by default:
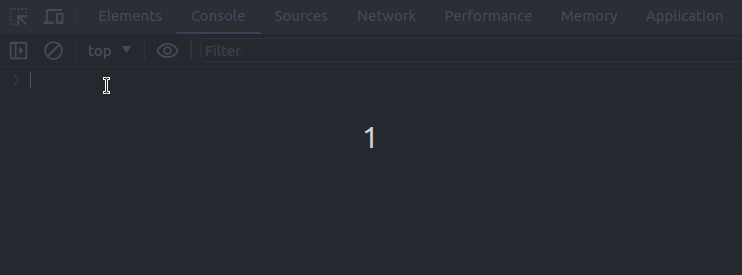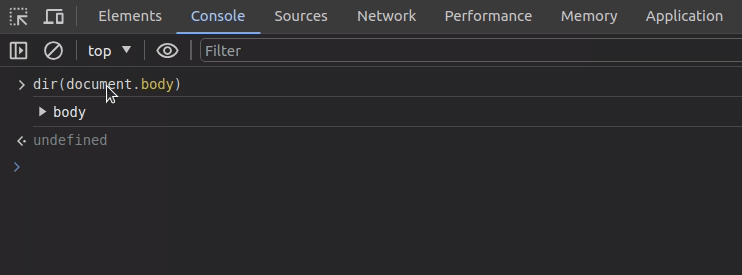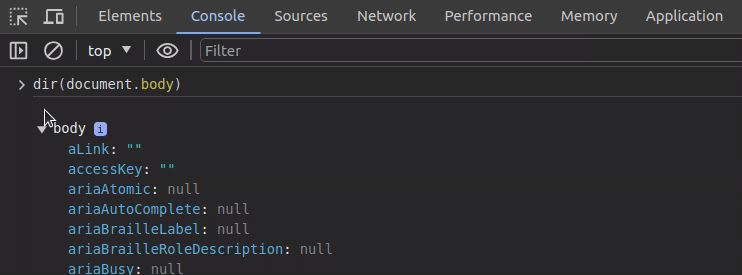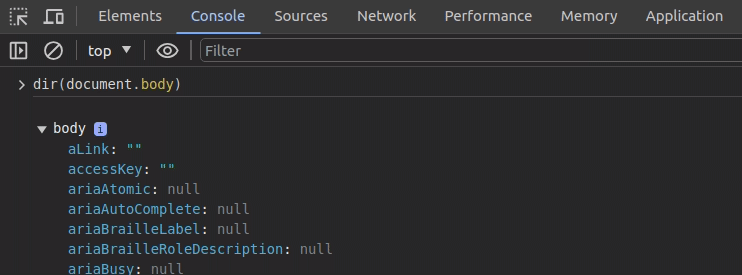
dir utility function in the Chrome console, a screen recording by the authorSimilarly, you can use the table function to use the console.table method. Also, the clear function invokes the console.clear method and clears the browser console.
The console API also offers two non-standard methods to start and stop the performance profiler. Chrome offers profile and profileEnd console function shortcuts to invoke these profiler-specific console API methods, as shown in the following preview:

Shortcuts for JS Object API
As a modern general-purpose programming language, JavaScript offers a fully-featured, pre-loaded standard library for almost all development requirements. JavaScript offers you a productive way to work with objects with a JSON-like object concept and provides an inbuilt JSON serializer/deserializer. Every web developer knows about Object.keys and Object.values methods that help us to extract keys and values from JavaScript objects. Chrome console utilities implement keys and values inbuilt function shortcuts and lets you productively use these frequently used Object API methods during debugging activities.
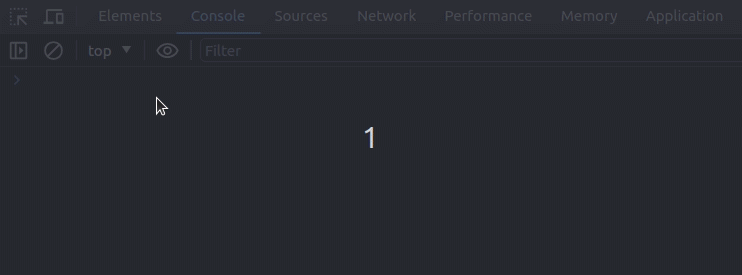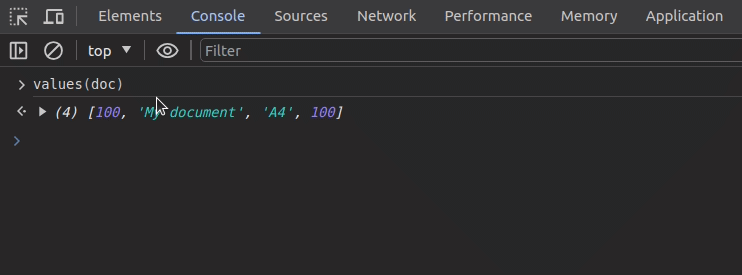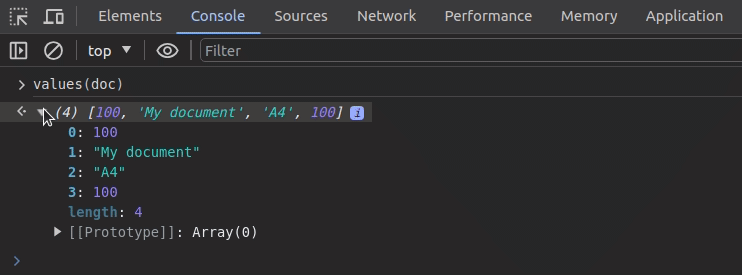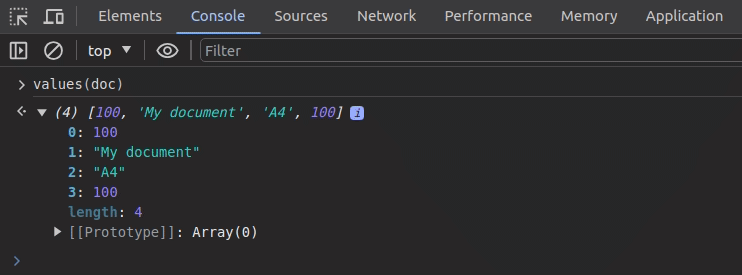
Assume that we need to inspect the following object’s keys and values separately:
const doc = {
id: 100,
title: 'My document',
size: 'A4',
authorId: 100
}You can print only the keys of the above object using the keys function, as shown in the following preview:
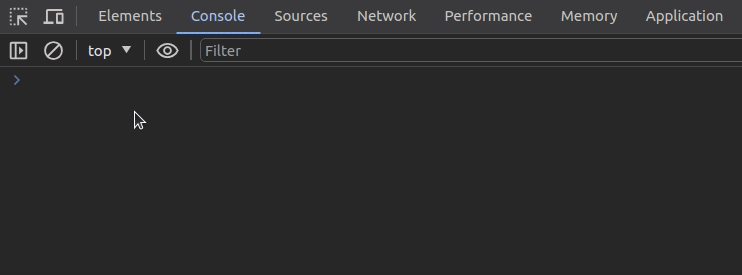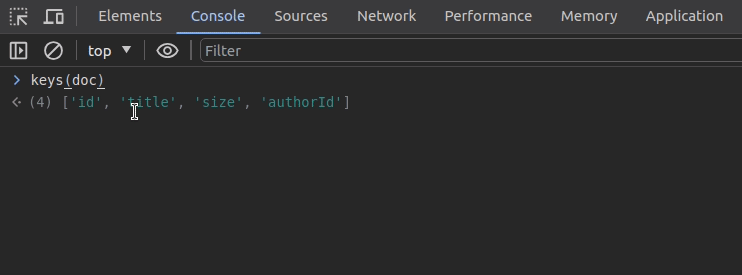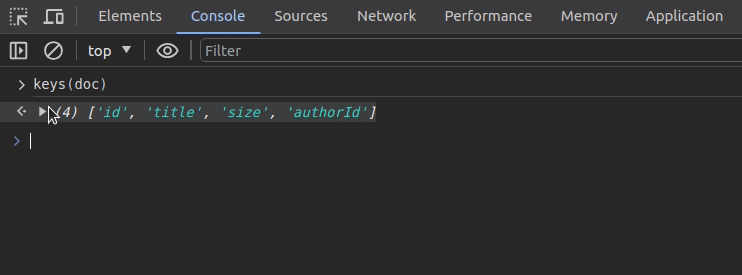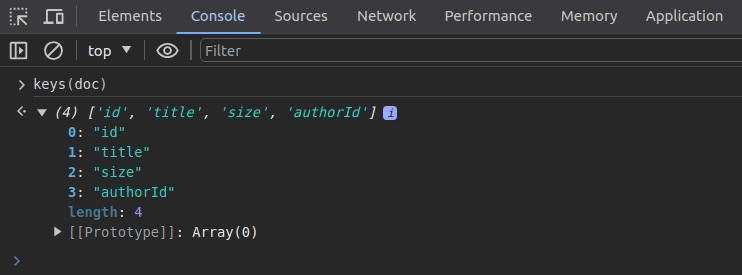
The values function offers a productive way to print all values of a specific object as follows:
The following story explains new browser APIs that you should know as an experienced web developer:
Set Breakpoints and handle code inspections with shortcuts
The modern web app debugging process typically involves using breakpoints and DOM inspections. Breakpoints help you debug JavaScript, and DOM inspections help you analyze HTML and improve CSS-based stylings. To set up breakpoints, we can use either the DevTools interface or the debugger JavaScript statement. Chrome console also offers productivity shortcuts to set up breakpoints.
Assume that the following function is loaded and available in the current console context:
function genArr(n) {
let sq = n ** 2;
sq = Math.min(sq, 1000);
let arr = [...new Array(sq).keys()];
return arr;
}Assume that you need to set a breakpoint within the genArr function. You can activate automatic breakpoints by calling the debug function on the console:
debug(genArr)Then, DevTools will automatically add a breakpoint for the genArr function:

Now, an automatic breakpoint halts code execution when the genArr function gets executed. It’s possible to deactivate automatic breakpoints with the following function call:
undebug(genArr)The above approach lets you set up breakpoints and browse functions. What if you need to check function sources without activating automatic breakpoints? The inspect function helps you navigate to a specific function. It also prints the source of the particular function on the console, as shown in the following preview:
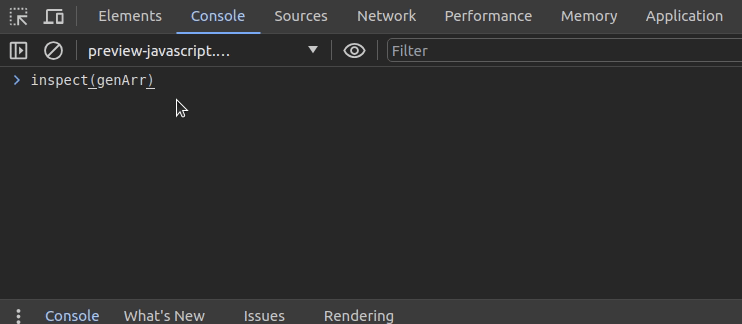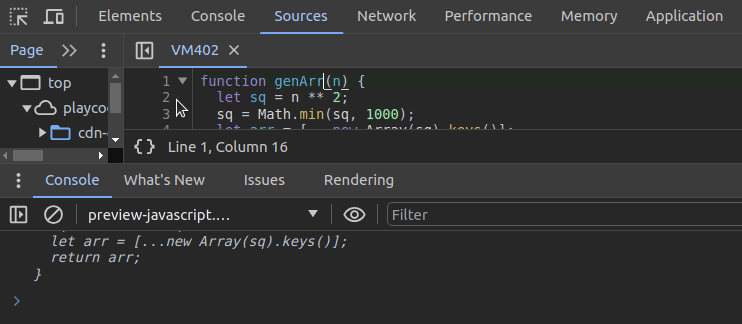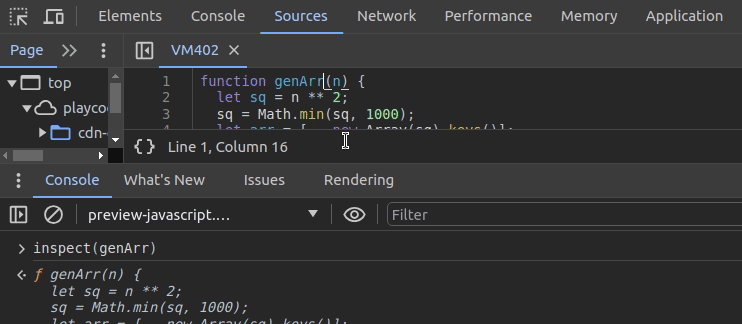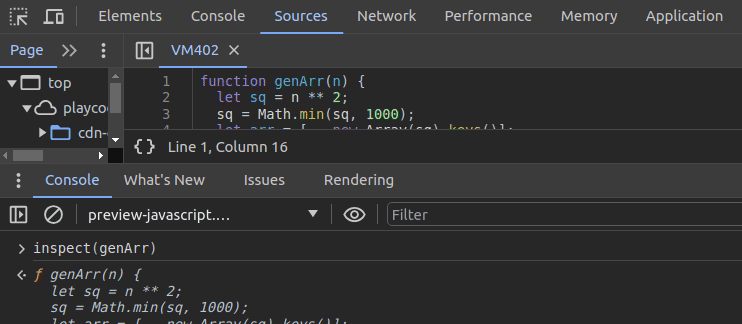
You can use the same function to inspect DOM elements. For example, the following code snippet starts inspecting the currently active element:
inspect(document.activeElement)Check Function Calls
There are several ways to detect function calls while doing a debugging task. Some developers typically use the console.log statement manually by printing some values on the console for detecting function calls. Meanwhile, some developers set up breakpoints. These approaches have several drawbacks. If a specific function gets called thousands of times, you will have a time-consuming job with breakpoints. On the other hand, you have to edit sources manually if you wish to use console.log-based approach.
Chrome console utilities offer monitor and unmonitor inbuilt console functions to productively monitor function calls without using breakpoints or editing source files manually.
Assume that you need to monitor the previous genArr function execution:
function genArr(n) {
let sq = n ** 2;
sq = Math.min(sq, 1000);
let arr = [...new Array(sq).keys()];
return arr;
}First, activate the monitoring feature for the particular function as follows:
monitor(genArr)Now, every call that comes to the genArr function is monitored and printed on the console with incoming arguments:
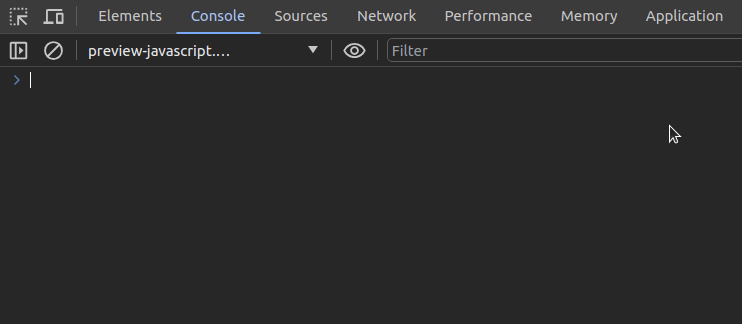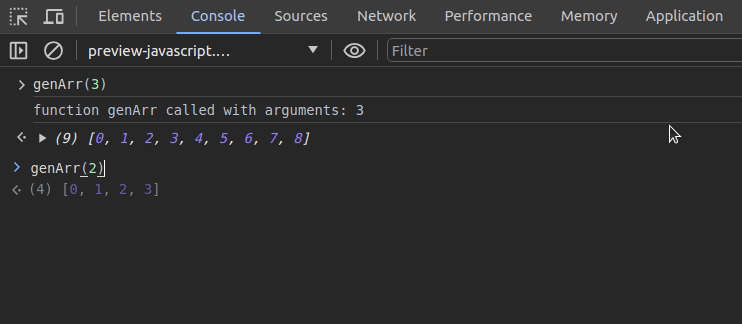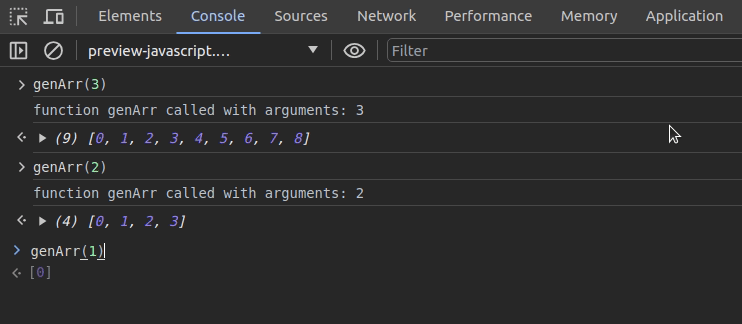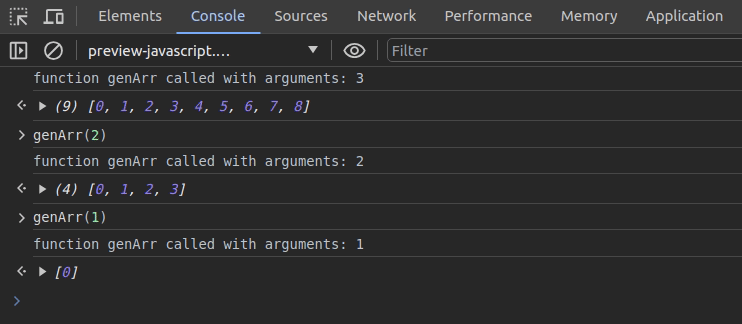
It’s possible to deactivate function monitoring for the genArr function with the following code snippet:
unmonitor(genArr)Working with Events Within the Console
DevTools offers several ways to detect browser events. It lets you set up event breakpoints that set source breakpoints automatically when a specific event gets triggered. Besides, it provides a feature to browse global events attached to the window object. What if you like to detect and browse web app events directly from the console?
Chrome console utilities offer the getEventListeners inbuilt function to find registered event listeners of a specific object. For example, the following code snippet prints all event listeners attached to the current active DOM element object:
getEventListeners(document.activeElement)The above utility function helps us browse registered event listeners, but how can we know when a specific event gets triggered without using the GUI-based event listener breakpoint feature in DevTools GUI?
The monitorEvents and unmonitorEvents shortcut functions let us monitor browser events based on JavaScript objects that capture events.
Look at the following code snippet:
monitorEvents(document.activeElement, 'click')Once you enter the above code snippet on the console, you can find all click events of the currently active element on the console:
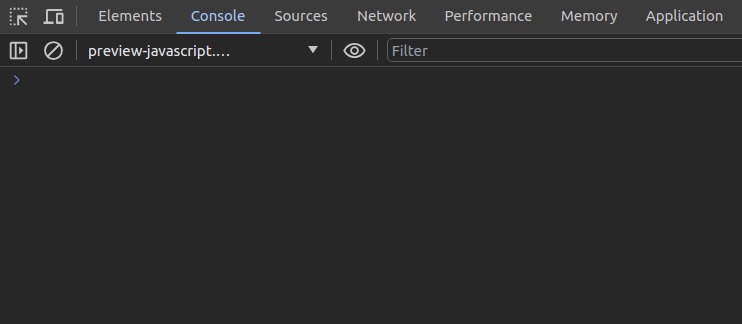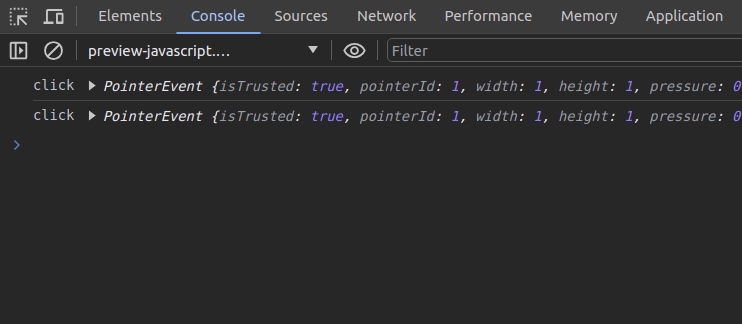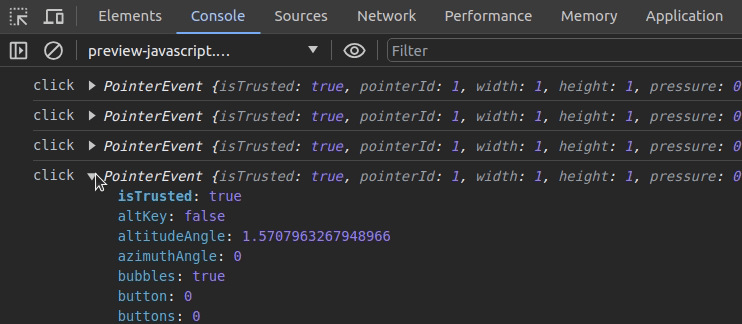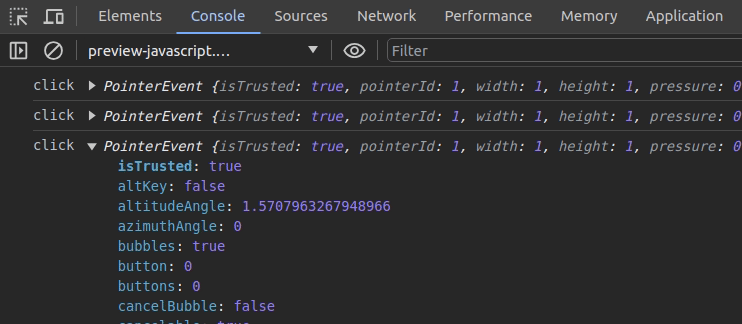
It’s possible to deactivate event monitoring with the following code snippet:
unmonitorEvents(document.activeElement)Variable syntactic sugar in Console
Every command-line interpreter typically offers various productivity-focused shortcuts to speed up development tasks. For example, the Bash interpreter offers the $? special parameter to get the exit code of the previous command’s process. Similarly, the Chrome console interpreter offers several shorthand variables for web app debugging tasks.
The $_ shorthand variable returns the return value of the previous expression executed on the console.
Look at the following example:
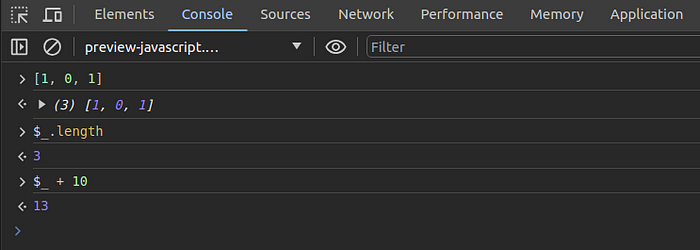
Earlier, we used the document.activeElement property and the $ query selector shortcut to refer to some DOM elements. However, developers tend to select DOM tree elements within the elements tab (inspector) without changing the focus of the real rendered DOM during debugging. So, if there is a shorthand variable to get the currently selected DOM element in the inspector, we can productively use it on the console without using document.activeElement or $-based selector syntax.
Chrome lets you refer to the selected DOM element in the inspector with the $0 shorthand variable. Assume that you need to change a data attribute of the selected DOM element via the console. You can do it as shown in the following preview:
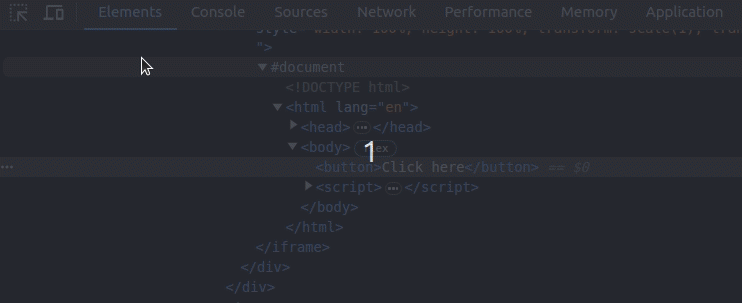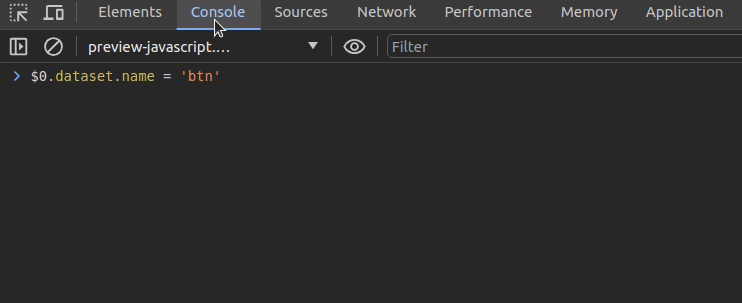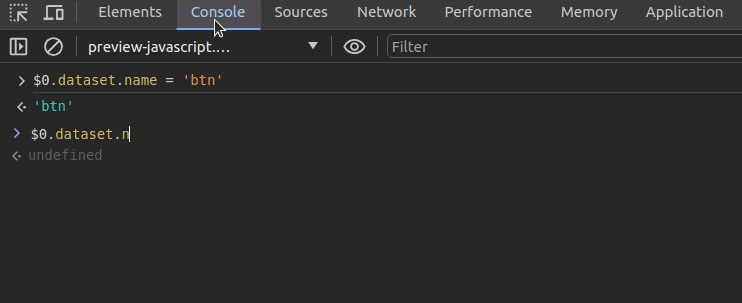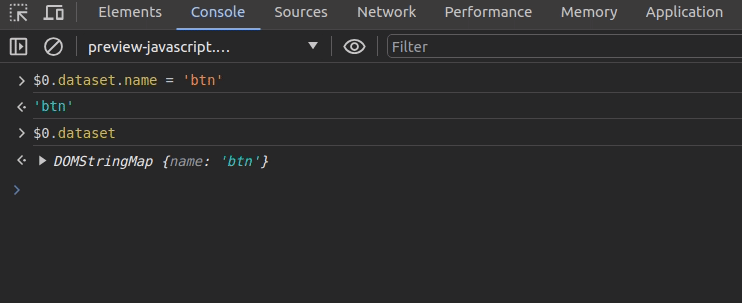
Let me reveal the bonus debugging tip of this article. You can use the copy function to copy a deserialized JavaScript object into the system clipboard.
Look at the following sample code snippet that copies a sample JavaScript object into the system clipboard:
const doc = {
id: 100,
title: 'My document',
size: 'A4',
authorId: 100
};
copy(doc);
No comments:
Post a Comment